TOPIC: Awareness in the Orbits fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
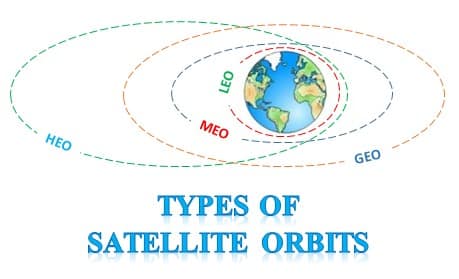
Types of Orbits according to shape
- Circular Orbit
- Elliptical Orbit
Types of orbits according to height ( Orbits )
- Low Earth Orbit- The altitude is between 160- 2,000 Km. For example, Hubble Space Telescope, International Space Station (ISS)
- Medium Earth Orbit- It is also known as Intermediate Circular Orbit (ICO). It lies above the LEO and below the geostationary orbit. 2,000 Km- 36,000 Km.
- Geostationary Orbit- The orbit is circular.
- – It is in the equatorial plane (directly above the equator and thus its inclination is zero).
- – The angular velocity of the satellite is equal to the angular velocity of the earth.
- – The period of revolution of the satellite is equal to the period of rotation of the Earth.
- – The satellite finishes one revolution around the Earth in exactly one day.
- – There is only one geostationary orbit.
- – It is also known as the Geostationary Earth Orbit or the Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit (GEO).
- – It is at a height of 36,000 Km from the Earth ( 35,786 Km to be precise).
- – The satellite follows the direction of Earth’s rotation.
- – The satellite appears stationary from the Earth.
- High Earth Orbit- It lies beyond 36,000 Km.
- Geosynchronous Orbit- It is not circular.
- – It is not in the equatorial plane but is in the inclined plane.
- – Angular velocity of the satellite is equal to the angular velocity of the Earth.
- – Period of revolution of the satellite is equal to the period of rotation of the Earth.
- – The satellite finishes one revolution around the Earth in exactly one day.
- – There are many geosynchronous orbits.
- Polar Orbit- It passes above or nearly above both the poles of the Earth.
- – It has an inclination of 90º to the equator.
- – The orbit is used for Earth mapping, Earth observation etc.
- – For Example, Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS).
- Sun Synchronized Orbit- It is a special case of the polar orbit.
- – The satellite travels from the North to South poles as the Earth turns below it.
- – The satellite passes over the same part of the Earth at roughly the same local time each day.
- – This orbit can make communication and various forms of data collection very convenient.
- – They are generally medium or low orbits.
- – Uses include for surface analysis and espionage.
- Example– Resource Satellites, Carto Satellites, Ocean Satellites.
- RISAT-1, RISAT-2 (Radar Imaging Satellite)
- RISAT-2 (a coastal surveillance satellite) was launched before RISAT-1(2012) in 2009 the aftermath of the 2008 Mumbai Terror Attacks.
- Indian Mini Satellite (IMS)- part of spying system
- Technology Experiment Satellite (TES)- It is also an IRS. It is an experimental satellite to demonstrate and validate, in orbit, technologies that could be used in the future satellites of ISRO.
Shifting Orbits
- When satellite reaches the apogee* position, an apogee motor is fired and the satellite moves to another orbit.
- * apogee- the point in the orbit of the moon or a satellite at which it is furthest from the earth.
Naming of satellites
- All geostationary satellites are called INSAT/GSAT i.e. Indian National Satellite used for communication, weather etc. They are launched using Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
- All remote sensing satellites are polar orbiting satellites. They are launched using a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). For example, CARTOSAT, RISAT, OCEANSAT, RESOURCESAT.
How are satellites disposed off?
There are two methods by which a satellite can be disposed off. Either of the two can be employed.
- Bring the satellite down to a lower orbit and burn it in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Take the satellite above its orbit and park it there.
- A height of ∼ 38,000 Km is known as the graveyard orbit/ junk or the disposal orbit.
- All geostationary satellites are shifted to this orbit after their useful life because they are too bulky to be brought down.
- Polar orbiting satellites are smaller in size and are at a lower height.
- So they are simply brought down as their volume is less.
- This makes them burn in the earth’s atmosphere.
How life of a satellite is calculated?
- The life of a satellite is calculated by the amount of fuel required by it to fulfill its functions.
- Once the fuel is finished, the satellite can be shifted above or below the orbit for disposal.
What is the fuel used?
- Mostly liquid fuel
- Methyl/ Ethyl Hydrazine
- It is toxic and dangerous if it falls on the population.
Also Read:-Scope of Artificial Intelligence in India: A Complete Guide